create project
使用IDEA创建一个scheduler-demo项目,这里可以使用spring initializr插件初始化spring boot

@EnableScheduling
注解EnableScheduling表示允许Spring Boot开启定时任务管理
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableScheduling
public class SchedulerDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SchedulerDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Scheduled
@Scheduled用来生成一个定时任务
@Scheduled的配置如下
| param | explain |
|---|---|
| fixedDelay | 两个定时任务之间的间隔,即前一个任务执行完后,延迟delay毫秒再执行下一个任务 |
| fixedDelayString | 与fixedDelay相同,只不过用string类型表示时间 |
| fixedRate | 固定周期执行任务,例如每隔10s执行一次任务 |
| fixedRateString | 与fixedRate相同,用string表示时间 |
| cron | 用cron表达式来管理定时任务 |
| initialDelay | 执行第一个定时任务的延迟时间,只对fixedDelay或fixedRate任务生效 |
| initialDelayString | 与initialDelay相同 |
| zone | 时区,默认使用server的时区 |
fixedDelay与fixedRate的区别
对于fixedDelay任务,后个任务一定需要在前一个任务执行完并且再过delay毫秒后才会执行。对于下面的例子来说,delay为5s,而任务执行需要5s,所有每隔10s任务才会执行一次
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 5000)
public void fixedDelayTask() throws Exception{
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm");
System.out.println(dateFormat.format(new Date()) + ":" + " task of fixed delay");
Thread.sleep(5000);
}

对于fixedRate任务,他们的执行是严格按照时间周期,即使上一个任务还未执行完毕,只要时间一到就会里面执行
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000,initialDelay = 5000)
public void fixedRateTask() throws Exception{
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(dateFormat.format(new Date()) + ":" + " task of fixed rate");
Thread.sleep(5000);
}

cron表达式
@Scheduled(cron = "[Seconds] [Minutes] [Hours] [Day of month] [Month] [Day of week]")
- second 取值在[0-59],或者特殊字符 , - * /
- minute 取值在[0-59], 或者特殊字符, - * /
- hour 取值在[0-23],或者特殊字符, - * /
- day of month 每个月第几天,取值在[0-31],或者特殊字段, - * / ?
- month 取值[1-12]或者月份的英文描述,特殊字符为, - * /
- day of week 取值为[1-7],1表示星期天,2表示星期一,以此类推,也可用英文描述的星期,例如SUN,特殊字符为, - * / #
| 特殊字符 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| * | 表示任意值,若second为*,表示每秒都会触发该事件 |
| , | 表示列出枚举值,若minute为5,20 则表示第5分钟和第20分钟会触发事件 |
| / | 表示起始时间开始触发,然后每隔固定周期都会触发,例如minute为5/20,则在5分,25分,45分都会触发事件 |
| - | 表示取值范围,若minute为5-20,则表示从5分到20分,每分钟都会触发事件 |
| ? | 只能用在每月第几天和星期两个域。表示不指定值,当2个子表达式其中之一被指定了值以后,为了避免冲突,需要将另一个子表达式的值设为”?” |
| L | 表示最后,只能出现在week或者day of month中,若week为1L,表示在最后一个星期天 |
| W | 表示有效工作日(周一到周五),只能出现在day of month中 |
| # | 用于确定每个月第几个星期几,只能出现在day of month中,例如1#3 表示每个月第三个星期日 |
cron示例
每天10点
0 0 10 * * *
每隔5分钟
* */5 * * * *
每天8点,8点半,9点,9点半,10点
* */30 8-10 * * *
自定义线程池来管理定时任务
自定义线程池配置,例如线程池size,线程池名称
@Configuration
public class ScheduleConfig implements SchedulingConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureTasks(ScheduledTaskRegistrar scheduledTaskRegistrar) {
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler taskScheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
taskScheduler.setPoolSize(10);
taskScheduler.setThreadNamePrefix("schedule-task-pool");
taskScheduler.initialize();
scheduledTaskRegistrar.setTaskScheduler(taskScheduler);
}
}
定义一个cron任务
@Scheduled(cron = "*/5 * * * * *")
public void cronTask(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(String.format("%s: current thread %s", dateFormat.format(new Date()), name));
}
运行程序,可以得到如下的运行结果,可以看到此时定时任务是运行在自定义的线程池里

动态管理定时任务
使用ThreadPoolTaskScheduler来生成定时任务,在通过维护定时任务的ScheduleFuture的map来实现动态管理定时任务
DynamicScheduleTaskManager
@Component
public class DynamicScheduleTaskManager {
private ThreadPoolTaskScheduler taskScheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
private Map<Integer, ScheduledFuture> futureMap = new HashMap<>();
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
taskScheduler.initialize();
}
/**
* 增加定时任务,若任务已存在,则删除旧任务,更新新任务
* @param taskConfig
*/
public void addOrUpdateTask(TaskConfig taskConfig){
int taskConfigId = taskConfig.getId();
if (futureMap.containsKey(taskConfigId)){
deleteTask(taskConfig);
}
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduledFuture = taskScheduler.schedule(() -> {
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String timeFormat = dateFormat.format(new Date());
System.out.println(String.format("time:%s,process task,id:%d",timeFormat,taskConfigId));
}, new CronTrigger(taskConfig.getCron()));
futureMap.put(taskConfigId, scheduledFuture);
}
/**
* 删除任务
* @param taskConfig
*/
public void deleteTask(TaskConfig taskConfig){
int taskConfigId = taskConfig.getId();
if (futureMap.containsKey(taskConfigId)){
ScheduledFuture scheduledFuture = futureMap.get(taskConfigId);
scheduledFuture.cancel(true);
System.out.println("delete task,id:" + taskConfigId);
}
}
}
TaskConfig
@Getter
@Setter
public class TaskConfig {
/**
* id of task
*/
private int id;
/**
* cron expression
*/
private String cron;
}
ScheduleController
@RestController
@RequestMapping(produces = "application/json; charset=utf-8")
public class ScheduleController {
@Autowired
private DynamicScheduleTaskManager scheduleTaskManager;
@PostMapping("/add/task")
public String addTask(@RequestBody TaskConfig taskConfig){
scheduleTaskManager.addOrUpdateTask(taskConfig);
return "success";
}
@PostMapping("/delete/task")
public void deleteTask(@RequestBody TaskConfig taskConfig){
scheduleTaskManager.deleteTask(taskConfig);
}
}
测试
####1. 新增taskConfig
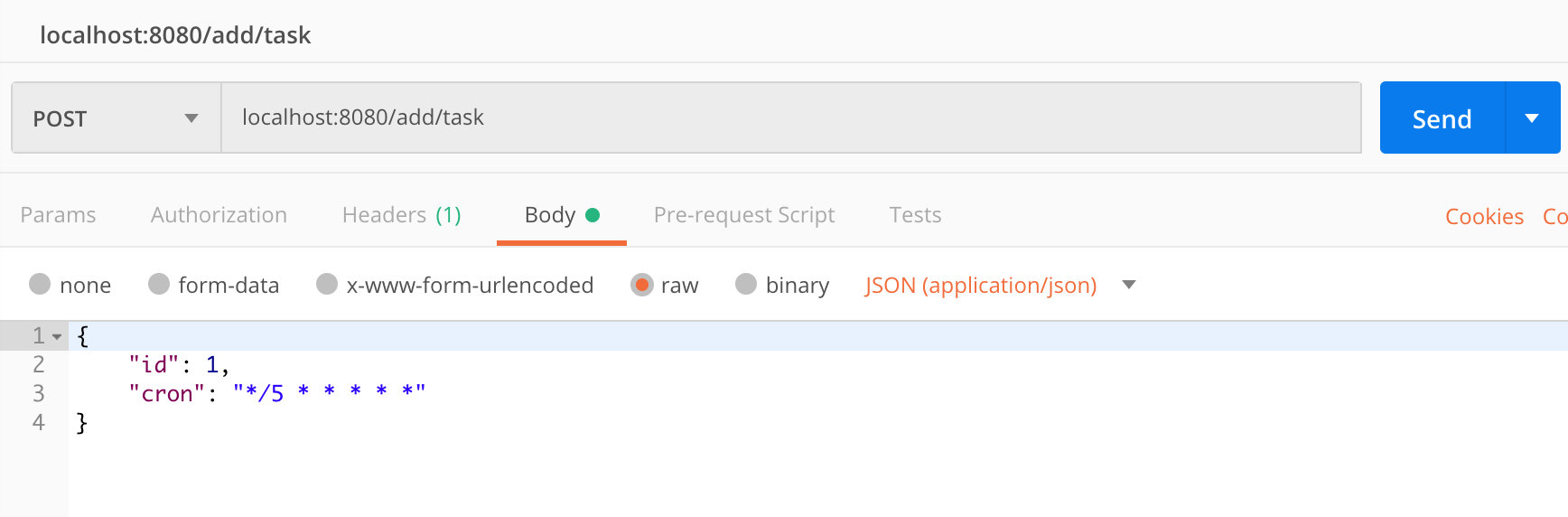
####2. 更新taskConfig

####3. 删除taskConfig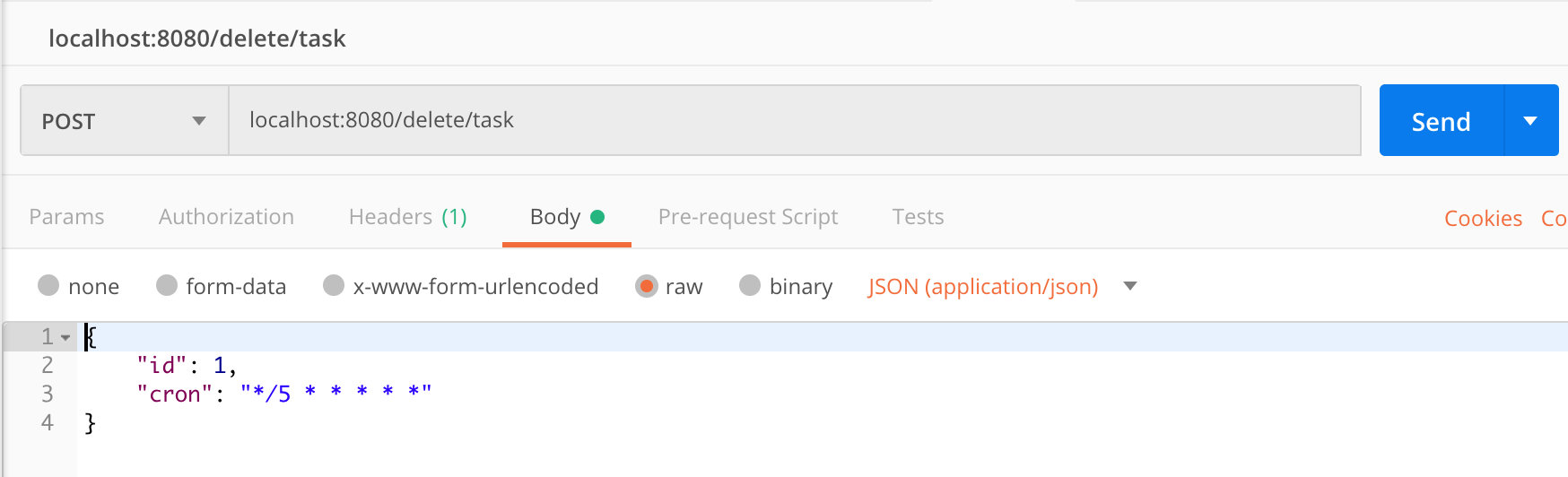
####4.输出




